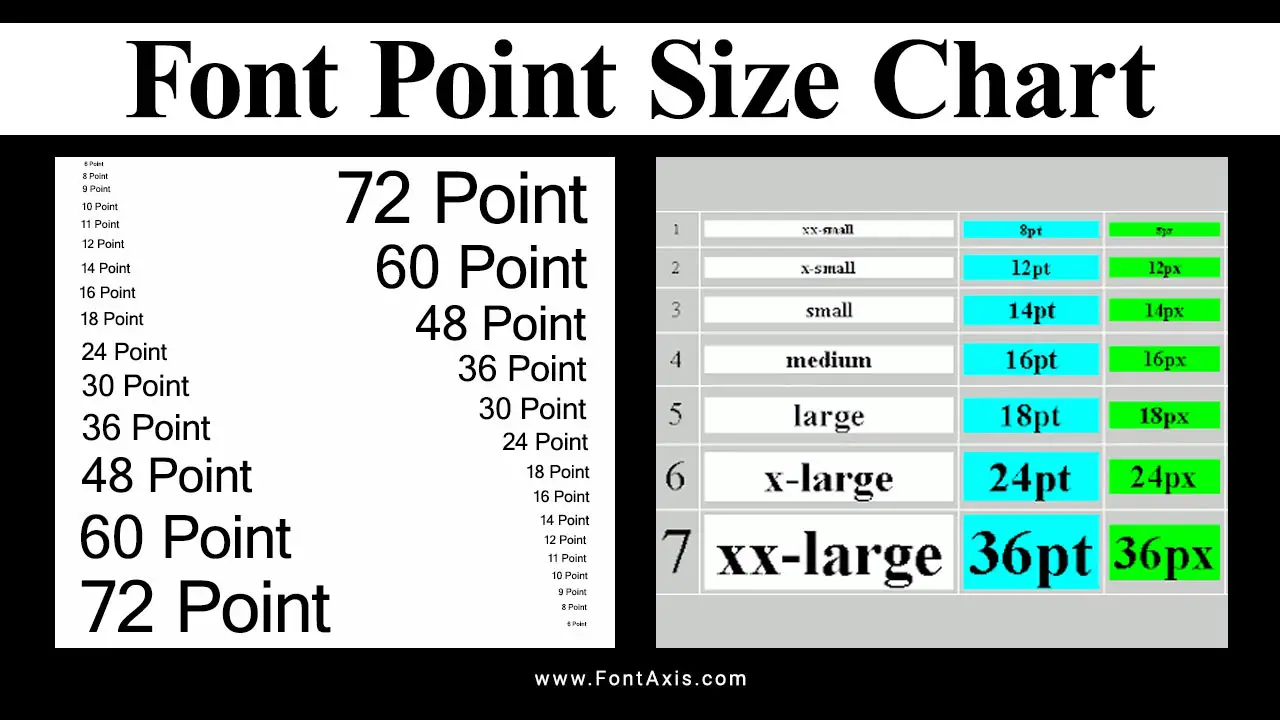
Font size measurement is essential in print and digital typography to ensure readability and legibility. The most common way to measure font size is in points (pt), but there are other units and methods depending on the context, such as print, screen, or web design. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you understand how to measure font size:

1. Understand Font Size Units
Before you start measuring, it’s essential to know the most common units used for font size:
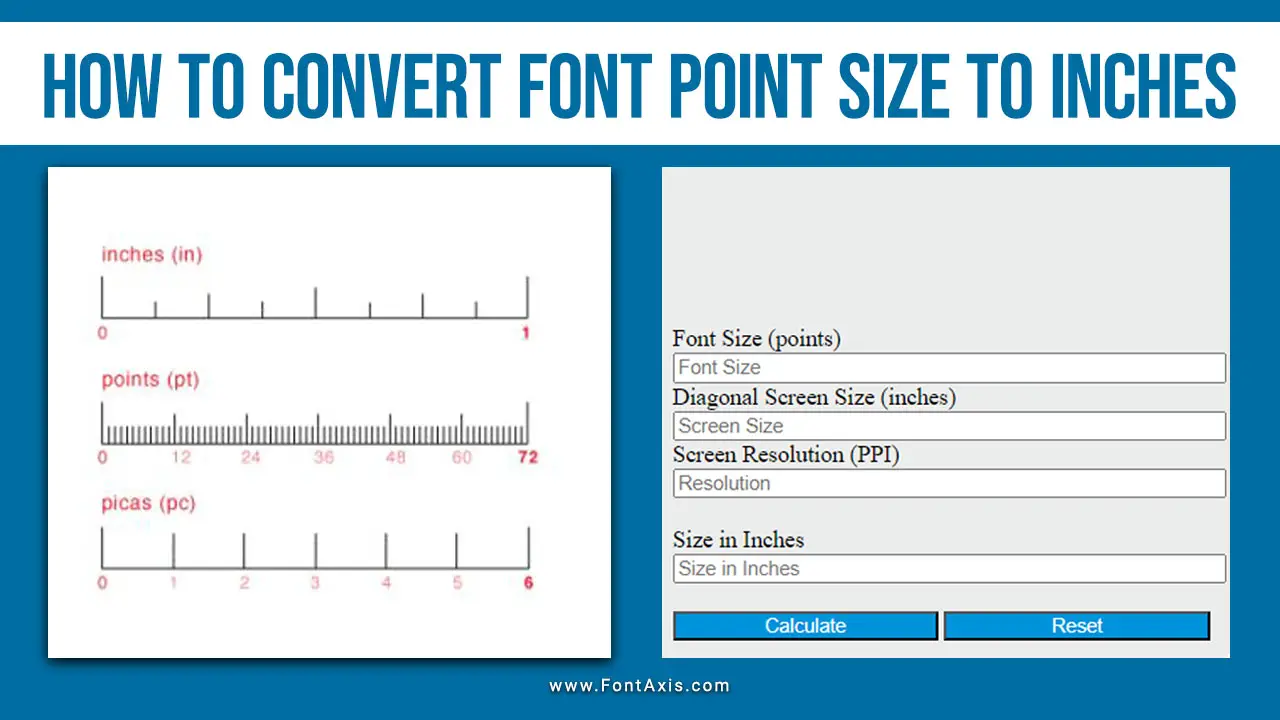
- Points (pt): The traditional unit in print. One point equals 1/72 of an inch.
- Pixels (px): Used primarily in digital screens. A pixel represents the smallest unit on a display.
- Em: A relative unit in web design that refers to the current size of the text or its parent element. One em equals the body text size (usually set at 16 px or 12 pt by default).
- Pica (pc): In print, 1 pica equals 1/6 of an inch (12 points).
- Percentage (%): Used in web design, where the size is a percentage of the parent element’s font size.
2. Measure Font Size In Points (For Print)

Traditionally, designers measure font size in points for print media:
- Step 1: Use a ruler to measure the height of the text from the baseline to the top of the tallest letter (cap height).
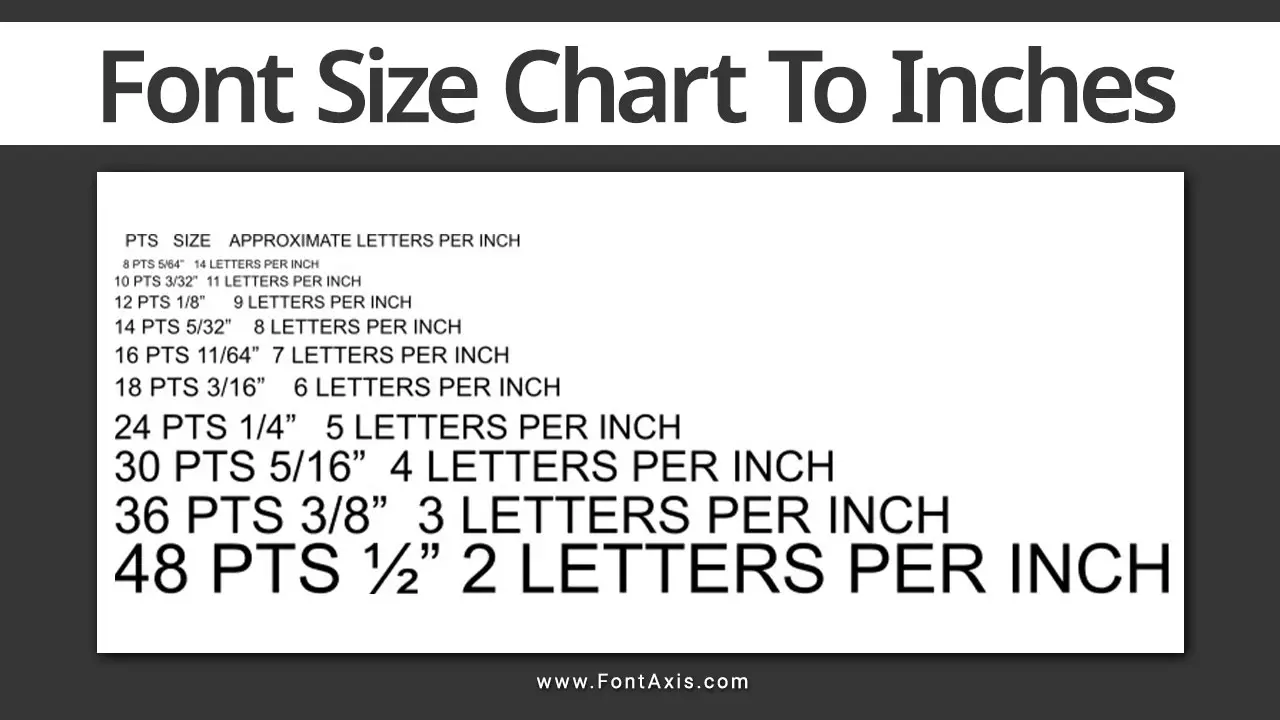
- Step 2: Convert the measurement to points using the conversion rate of 1 point = 1/72 of an inch.
For example, if the text height is 1 inch, the font size is 72 points. A smaller text with a height of 1/6 inch would be 12 points.
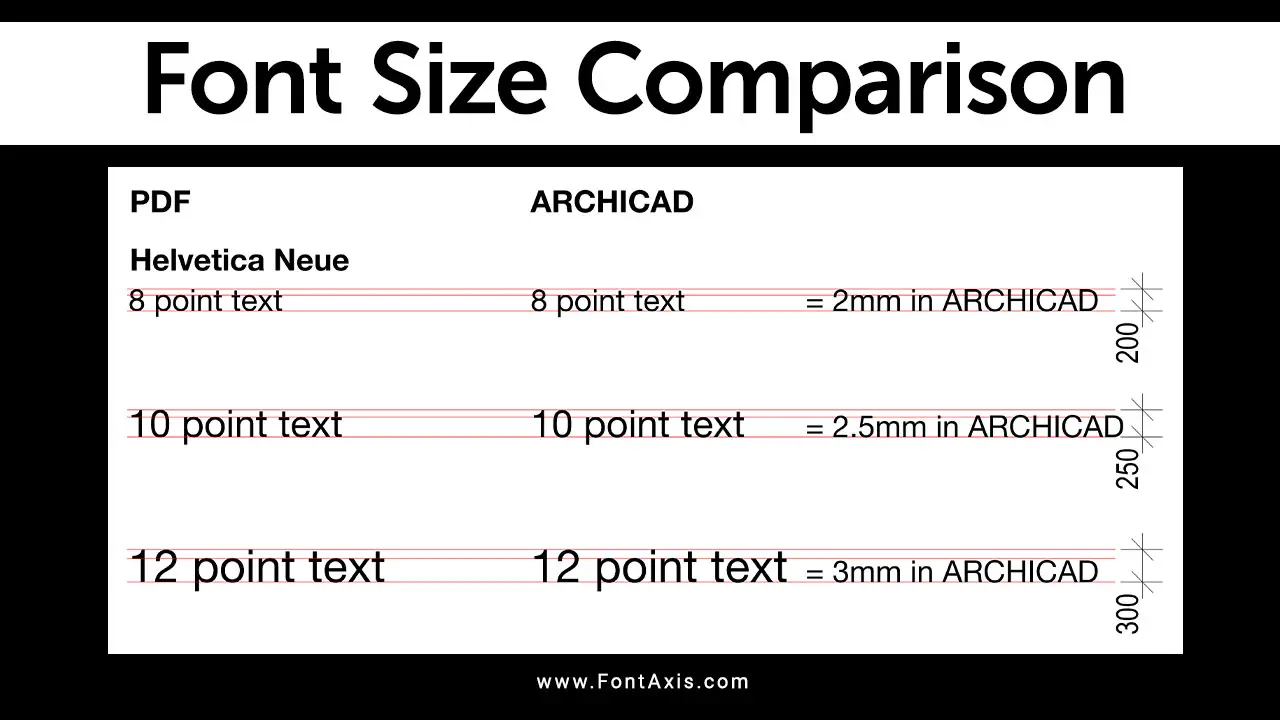
3. Convert Millimeters To Points
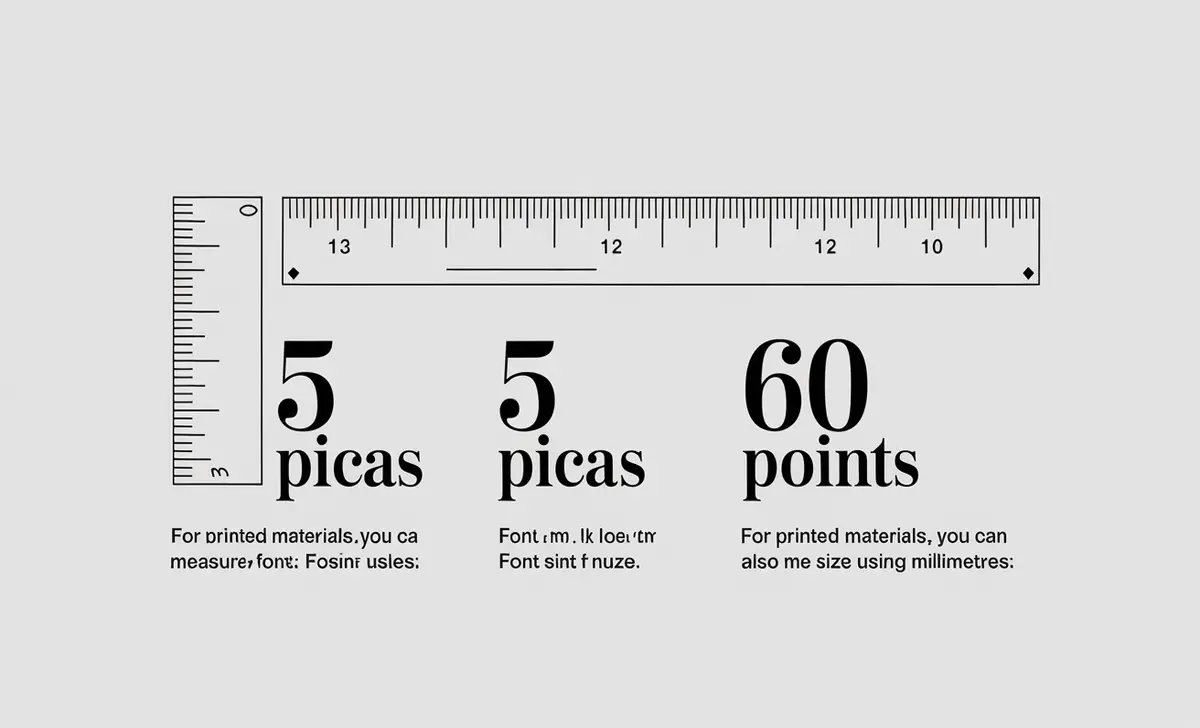
For printed materials, you can also measure font size using millimetres:
- Step 1: Measure the font height in millimetres from the baseline to the top of the tallest character.
- Step 2: Divide the height (in millimetres) by 4.217 to convert it into picas.
- Step 3: Multiply the result by 12 to convert the picas to points (since 1 pica = 12 points).
Example:
- If the height is 21.085 mm, divide by 4.217 to get 5 picas.
- Multiply 5 picas by 12 to get a font size of 60 points.
4. Measure Font Size In Pixels (For Digital Type)
![]()
For digital displays, font size is often measured in pixels:
- Step 1: Most screens use pixels as the smallest unit of measurement. A standard default font size for body text on web pages is 16 px.
- Step 2: Use a design or browser developer tool to inspect the text element and see the font size in pixels.
5. Use Relative Units For Web Typography

Web designers often set font sizes using relative units like em and percentages:
- Step 1: Designers usually set the body text to a default size of 16 px or 12 pt.
- Step 2: Using em or percentages, you can set the size of other text elements (like headings) relative to the body text size. For example, 2em would mean twice the size of the body font, while 100% would mean the same size as the body text.
6. Consider Viewing Distance

The viewing distance plays a significant role in determining font size:
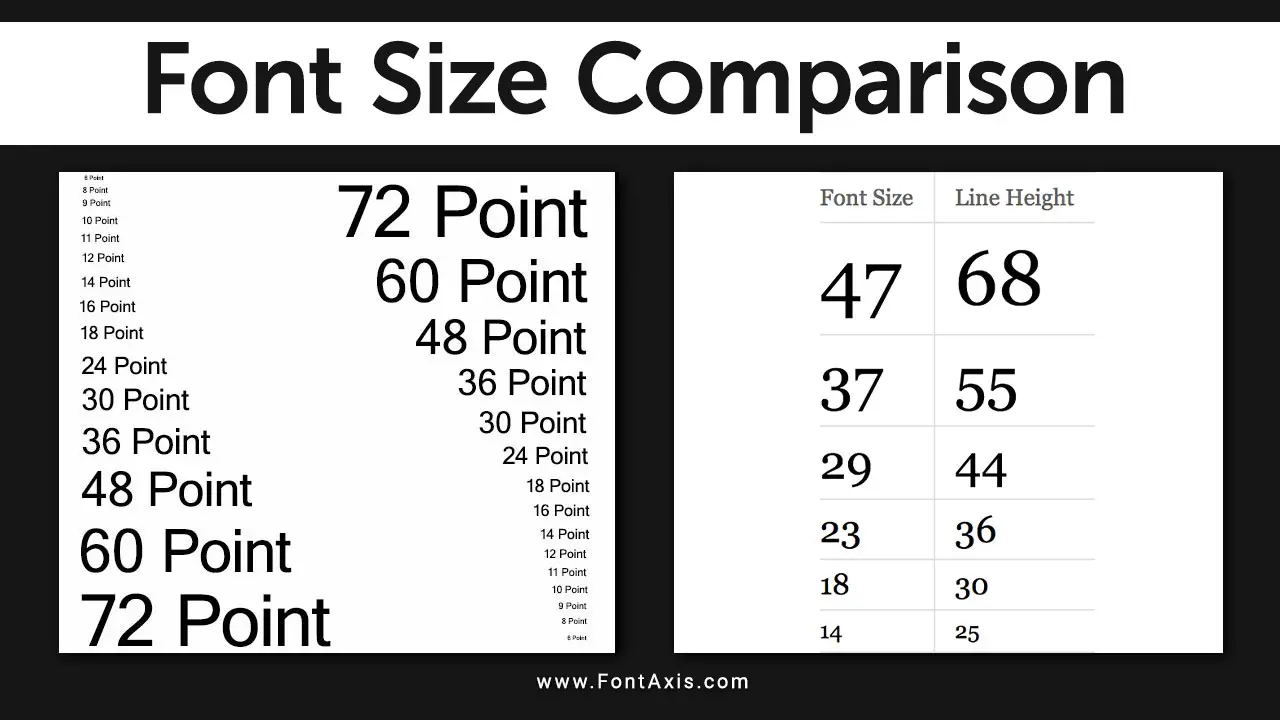
- Step 1: For printed materials like books, designers typically use a body font size of 10-12 pt because readers view the text up close.
- Step 2: The font size should be much larger for large displays like posters or billboards because the viewing distance is greater. Designers commonly use font sizes of 72 pt or more for large text seen from far away.
7. Use Software Tools For Precise Measurement
For documents in word processors like Microsoft Word, you can set the font size directly:
- Step 1: Select the text element in your document.
- Step 2: Select the appropriate size in the font size dropdown (e.g., 12 pt for body text).
In design software like Adobe Illustrator or InDesign, you can adjust the font size in points, pixels, or em, depending on the project.
8. Measure Type Size In Metal Type

In traditional metal type (used in old printing presses), the type size refers to the size of the metal block that holds the letter, not the letter itself. The block size is measured in points, so if you are working with vintage printing, the font size corresponds to the height of these blocks.
Conclusion
Understanding how to measure font size is crucial for designers to create functional and aesthetically pleasing designs. Whether you’re working on print or digital media, choosing the right size for your text elements helps ensure your audience can easily engage with your content. By considering factors like line length, visual hierarchy, and the needs of readers with visual impairments, you can create text that is accessible, legible, and effective.
FAQs
1.What Is The Standard Body Font Size For Web Design?
The default font size for body text in web design is typically set at 16 px, which balances readability and legibility on most screens.
2.How Is Font Size Measured In Typography?
Font size is usually measured in points (pt), with one point equaling 1/72 of an inch. Other units, such as pixels (px) and ems, are common in digital and web typography.
3.What Is The Difference Between Absolute And Relative Units In Font Sizing?
Absolute units like points or pixels define the fixed size of the font, while relative units like ems or percentages scale based on the parent element’s size, making them more adaptable for responsive design.
4.How Does Viewing Distance Affect Font Size?
The further the reader is from the text, the larger the font must remain legible. For instance, fonts on billboards must be much larger than those in books to account for the increased viewing distance.
5.How Do Different Fonts Affect The Perceived Size Of Text?
Fonts vary in design, with some appearing larger or smaller, even at the same point size. For example, a 12 pt serif font may look larger than a 12 pt sans-serif font due to differences in body height and characters’ structure.