When developing desktop applications using Python, Tkinter is one of the most popular tools for creating graphical user interfaces (GUI). One crucial aspect of GUI development is selecting the right font, which impacts readability and aesthetics.
In this guide, we’ll explore choosing the perfect font for your Tkinter application, including how to manipulate fonts for various Tkinter widgets like the text widget, label widget, and entry widget.
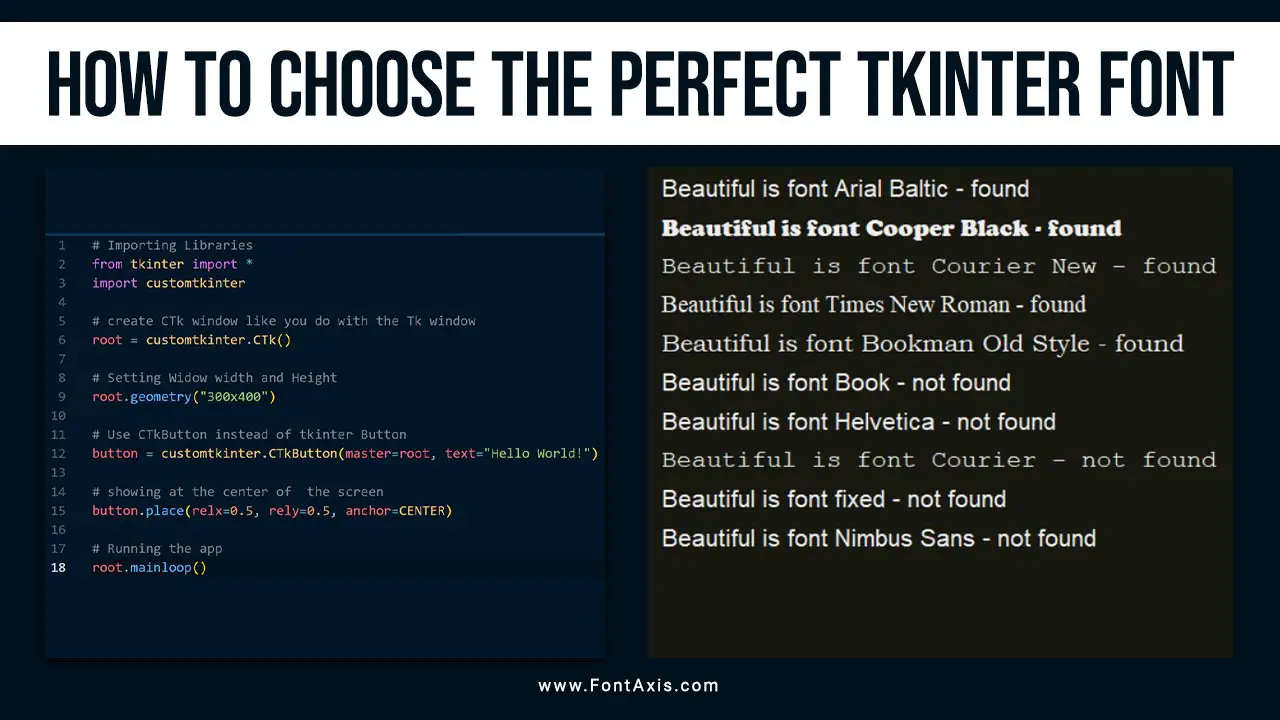
How To Choose The Right Tkinter Font

Selecting the right font is crucial for creating effective and user-friendly Tkinter applications. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to choose the perfect Tkinter font:
1. Consider The Widget Type
Different widgets might require different fonts. The text widget, label widget, and entry widget commonly display text, but each serves a unique purpose.
- Text Widget: This widget displays multiple lines of text. A legible and clean font like Arial or Times New Roman works well here.
- Label Widget: This is typically used for short pieces of text like labels or headers. A bold or italic font style can make labels stand out.
- Entry Widget: For input fields, a clean and modern font, such as Helvetica, enhances readability.
2. Choose The Right Font Family

Choosing a suitable font family is essential for ensuring the readability of your application. Tkinter supports many system fonts, but sticking to commonly used fonts like Arial, Courier, or Times New Roman ensures consistency across different systems. If the desired font is unavailable, a fallback font will be used.
3. Set Appropriate Font Size

The font size should be set according to the purpose of the text. A default value of 10–12 pixels works well for most general text, but larger font sizes (e.g., 16–24 pixels) make text more prominent for headers.
Pythonlabel = Label(root, text="Welcome", font=("Arial", 20)) # Large font for headersWhen designing for modern, high-resolution displays, make sure the font height and pixel size are sufficient for clarity.
4. Adjust Font Style And Weight

Tkinter allows you to define text in bold, italic, or underlined styles by specifying the font style. For example:
Pythonfont_style = ("Times New Roman", 12, "italic")This can be used to emphasize certain parts of your UI, such as headers, warnings, or selected text.
5. Font Color And Background
The foreground and background color of the text can be customized using the fg and bg attributes. This is particularly useful for contrasting the text and the Tkinter window background.
Pythonlabel = Label(root, text="Colored Text", font=("Arial", 14), fg="blue", bg="yellow")In this example, the text color (foreground) is blue, and the background color is yellow.
6. Testing Fonts Across Platforms
While Tkinter provides a default font for your system, it is important to test your Tkinter application across different platforms (Windows, macOS, Linux) as fonts may render differently. This is where a fallback font comes in handy, ensuring that the text remains readable even if the preferred font is unavailable.
Conclusion
Choosing the right font for your Tkinter application significantly impacts both usability and aesthetics. By understanding how to manipulate font objects, size, family, and style, you can create polished desktop applications that offer a better user experience. Test your fonts across platforms and adjust the foreground and background colors to enhance readability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1.What Is The Default Font In Tkinter?
The default font depends on the system, but it’s usually a basic system font like TkDefaultFont.
2.How Do I Change The Font In A Tkinter Text Widget?
You can set the font using the font attribute, for example: text_widget = Text(root, font=(“Arial”, 12)).
3.Can I Use Custom Fonts In Tkinter?
Yes, you can specify any installed system font. If the font is not available, a fallback font will be used.
4.How Do I Change The Color Of The Text In Tkinter?
Use the fg attribute to set the text color, for example: label = Label(root, text=”Hello”, fg=”blue”).
5.Can I Use Multiple Fonts In The Same Widget?
Yes, particularly in a text widget, you can use tags to apply different fonts to different text parts.
